
Asthma Medication in Australia: A Quick Guide
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways, making it difficult to breathe. In Australia, it's a significant health concern, affecting about 11% of the population. Managing asthma effectively is crucial, and this largely depends on the right medication and...

Asthma Treatment Australia with A for Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing difficulty in breathing and wheezing. In Australia, asthma is prevalent, with a significant portion of the population experiencing its effects. Understanding the various...

Natural Remedies for Asthma: Breathing Easier with an Alternative Approach
Asthma is a condition that robs you of breath and peace of mind. For those who've struggled to control its symptoms under the weight of pharmaceutical regimens, the allure of natural remedies is undeniable. Enter "A for Asthma," a new wave of health advocacy touting...
Vitamin A
The deep yellow pigment in most fruits and vegetables can be attributed to Beta-carotene, the precursor to Vitamin A. Beta-carotene can be metabolised to vitamin A in the human body but only one sixth of dietary beta-carotene is converted to Vitamin A. The best source of Vitamin A is fish and animal products: liver, oily fish – such as halibut, herring, tuna, pilchards and sardines. Here are some important functions of vitamin A:
- Vitamin A maintains healthy Skin and mucous membranes – helping to prevent against Infection of the nose, throat, lungs, urinary tract etc.
- The vitamin is necessary in the formation of visual purple, an eye pigment involved in night vision.
- Vitamin A is needed for proper development of the foetus in the womb. It also influences proper bone development.
DEFICIENCY
Severe vitamin A deficiency leads to various physical changes in the eye and eventually leads to blindness. A marginal vitamin A deficiency will lead to increased susceptibility to respiratory tract Infections and skin problems.
BENEFITS
Vitamin A has also been used successfully in the treatment of certain Skin conditions, e.g. Acne and Psoriasis (1,2).
VITAMIN A & ASTHMA
Use of vitamin A supplements have been shown to be beneficial to respiratory tract infections. The use of Vitamin A with vitamins C & E are a good combination for asthma prevention.
SOURCE OF VITAMIN A
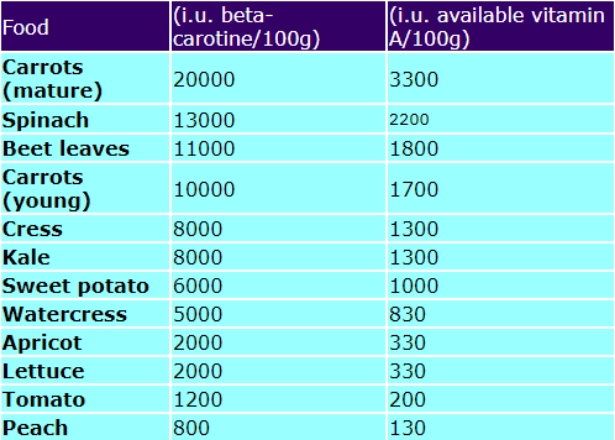
The main sources of vitamin A in the diet are animal products: milk, fortified margarines, cheese, egg yolk, liver, oily fish – such as herring, tuna, pilchards and sardines. Vitamin A (as beta-carotene) is found in carrots, tomatoes, red peppers, green leafy vegetables, mangoes, apricots, broccoli, sweet potatoes. Table 1 shows the animal foods and vitamin A. These are better sources for vitamin A since no conversion is required by the body. Fruits and vegetables are listed in Table 2, but note the available vitamin A content is only one sixth the beta-carotene level. Diabetics are incapable of converting carotene to vitamin A.
Table 1: Animal foods and vitamin A content:
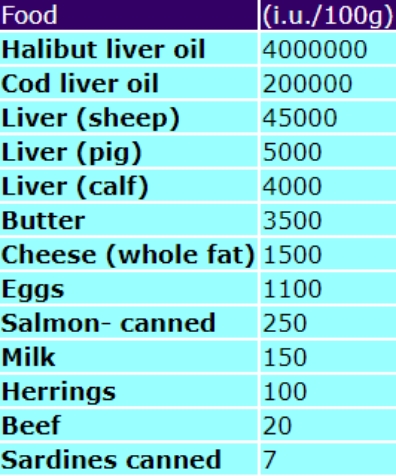
Table 2: Fruits and vegetables and beta-carotene + available Vitamin A.
REFERENCES
- Futoryan T, Gilchrest BA. Retinoids and the skin. Nutr Rev, 52;9:299-310, 1994.
- Fleischer AB Jr et al. Alternative therapy is commonly used within a population of patients with Psoriasis. Cutis, 58;3:216-220, 1996.
- Tables 1 & 2 data extracted from “Give Asthma the Big A” Marian Shepherd Slee.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin present in almost all plant and animals. Humans (and other high primates), cannot produce their own body supply of vitamin C, and therefore require a dietary intake. The vitamin is required for many body functions. Here is a list of some bodily processes where vitamin C is involved:
- Formation of collagen – the body’s intracellular “cement”
- Growth, tissue repair and healing
- Formation of antibodies and stimulation of the white blood cells
- Formation of corticosteroid hormones in the adrenal gland
- Absorption of ..and its necessary accumulation in the bone marrow, spleen and liver.
- As an antioxidant nutrient, it protects water-soluble substances from oxidation by allowing itself to be oxidised.
- As an anti-histamine, vitamin C reduces the effect of histamine produced by the immune system. Histamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of allergies such hay fever.
- Carnitine formation in vegetarians, together with lysine.
DEFICIENCY
Lack of vitamin C in a regular diet can cause a deficiency disease known as scurvy. The symptoms include bleeding of the gums and loosening of the teeth, together with lassitude, weakness, irritability and muscle ache. The recommended daily allowance of vitamin C is set at 60mg.
BENEFITS
Studies have shown that vitamin C levels become depleted during infection. An increase to 1 gram a day has been shown to help symptoms of the common cold. Asthmatics have reduced levels of vitamin C in their blood (1). Use of vitamin C supplements have been shown to reduce the severity of asthma attacks(2) and protect against exercise induced asthma(3).
Sources of Vitamin C
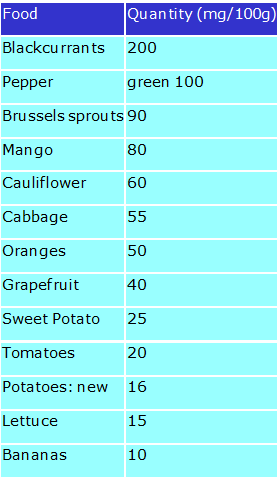
The main sources of vitamin C in the diet are potatoes, fruit juices, citrus fruit and green vegetables. The vitamin C content of foods varies very widely depending upon season, variety and freshness.
Foods and vitamin C content:
REFERENCES
- “Healing Through Nutrition”, Dr M Werbach, Thorsons, 1993.
- Anah CO, Jarike LN and Baig HA> High dose ascorbic acid in Nigerian Asthmatics. Trop Geograph Med, 32:132-137, 1980.
- Schachter EN and Schlesinger A. The attenuation of exercise-induced bronchospasm by ascorbic acid.. Ann Allergy, 49:146-150, 1982.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is also commonly used as a supplement to improve dry skin. Although there is no definite basis for its use in skin care, anecdotal reports do indicate it may be of benefit. Vitamin E is a constituent of many beauty creams that are applied to the face.
Vitamin E is measured as mg or international units (1 mg = 1.49 i.u).
DEFICIENCY
Deficiency of vitamin E in the diet has no defined disease but chronic deficiency has been implicated as a contributor to cancer and heart disease.
BENEFITS
The recommended daily allowance of Vitamin E is 10mg per day but the upper safe level for daily supplementation = 800mg (1200i.u.). Together with Vitamins C and A they are known as the’anti-oxidant group’. The combination is also important for prevention of respiratory ailments and asthma.
Vitamin E supplements may help with a range of conditions:
- Heart conditions (2)
- Circulatory disorders(3)
- Fibrocystic breast disease (4)
- Blood platelet aggregation (e.g. in susceptible women on the contraceptive pill) (5)
- Vitamin E may also be used as a nutritional therapy in the following conditions:
- Pre-menstrual syndrome (6) (especially with Evening Primrose Oil)
- Post-operative Wound healing (7)
- Poor circulation (3), Varicose veins, etc.
- Alzheimer’s disease (8)
Sources of Vitamin E
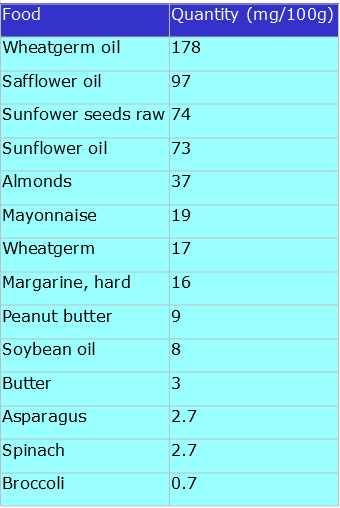
The main sources of vitamin E in the diet are wheat-germ oil, wheatgerm, almonds and oil seeds.
Foods and vitamin E content:
REFERENCES
- “Human Nutrition and Dietetics”, J S Garrow & W P T James, Churchill Livingstone, 1996.
- Kwiterovich PO Jr. The effect of dietary fat, Antioxidants, and pro-oxidants on blood lipids, lipoproteins, and Atherosclerosis. J Am Diet Assoc, 97;7 suppl:S31-41, 1997.
- “Martindale The Extra Pharmacopoeia”, J Reynolds, The Pharmaceutical Press, 29th Ed, 1989.
- London RS et al. Endocrine parameters and alpha-tocopherol therapy of patients with mammary dysplasia. Caner Res, 41:3811-3813, 1981.
- Renaud S et al. Influence of vitamin E administration on platelet functions in hormonal contraceptive users. Contraception, 36:347-358, 1987.
- London RS et al. Efficacy of alpha-tocopherol in the treatment of the premenstrual syndrome. J Reprod Med, 32;6:400-404, 1987.
- Int J Dermatol, 1995,34;7:506-509.
- Sano et al. A controlled clinical trial of Selegiline, Alpha-tocopherol or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. New England J Med, 336;17:1216-1222, 1997.
